Hydrogen Production
5 min read
is the most abundant chemical element in the universe, found in the Sun, other stars and the gas planets in our solar system. It occurs naturally on Earth, but not in large enough quantities to be produced cost-competitively. It therefore needs to be separated from other elements.

© Labelle Michel / TotalEnergies - A steam methane reformer used to produce hydrogen at the Jubail refinery in Saudi Arabia.
On Earth, hydrogen is generally found in compounds with other elements. The most common are carbon, with which it forms , and oxygen, with which it forms water (H2O). How is pure hydrogen made? To obtain pure hydrogen for industrial applications, it must be separated from the chemical elements to which it is bound.
Hydrogen Production Process Technologies
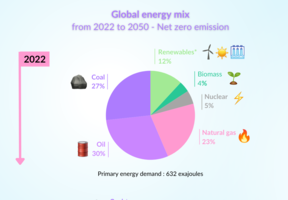
Today, 95% of hydrogen is produced either from wood or from fossil fuels, such as natural gas and oil. Three types of production process are currently in use:
- The most common hydrogen production process is natural gas reforming — sometimes called steam methane reforming because it uses high-temperature steam. When exposed to steam and , the carbon (C) atoms of methane (CH4) separate. After two successive reactions, they reform separately to produce hydrogen (H2) and carbon dioxide ( ). This operation therefore requires natural gas.
- Another process is gasification1. Charcoal consists mainly of carbon and water. Burned in a reactor at a very high temperature of between 1,200 and 1,500 °C, the charcoal releases gas that separates and reforms to produce hydrogen (H2) and (CO).
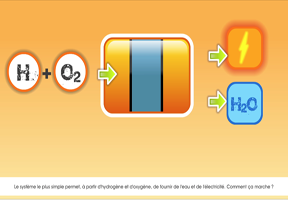
- Hydrogen can also be produced using , through electrolysis of water. An electric current is used to split water (H2O) into oxygen (O2) and hydrogen (H2). This method is not as cost-effective as using fossil fuels. Hydrogen produced by steam methane reforming costs around €1.5 per kilogram at the plant gate (excluding distribution costs), triple the cost of natural gas. Hydrogen produced using electrolysis is currently around four times more expensive, even before the cost of the electricity required is factored in.
Only 1% of the hydrogen produced in France is obtained using electrolysis technology. But as new uses for hydrogen energy emerge, requiring purer hydrogen, the horizons for this technology are broadening. R&D work aims to lower production costs, especially by using high-temperature (or steam) electrolysis at 700 to 800 °C.
Producing “Clean” Hydrogen
To ensure that this new is “green” — meaning that it emits little greenhouse gas — hydrogen production has to be as clean as possible.
Reforming produces few greenhouse gases when combined with carbon capture and storage processes; however, these significantly increase costs.
Gasification is another option, because it covers the entire solid pathway: many types of organic matter can be burned to produce . Although wood (in the form of charcoal) is the main feedstock used, plant waste such as straw is also suitable. Because biomass sources can be replanted, the is low.
Electrolysis also produces clean hydrogen when “green” electricity is used. But to overcome the issue of cost-competitiveness, large amounts of inexpensive electricity are needed year-round. Prototypes are under study, especially in Germany, to use intermittent production spikes from wind and solar energy. But for now, the cost of electrolysis is still prohibitive.
Other hydrogen production processes are also being examined
- Some modified microorganisms can produce hydrogen when exposed to sunlight, a process known as biological hydrogen production by photosynthetic microorganisms.
- In photoelectrolysis, a photoelectrochemical cell submerged in water uses sunlight to separate the water into hydrogen and oxygen bubbles.
- In the thermochemical cycle, water is heated to 800 to 1,000 °C, with the splitting to release hydrogen. The main drawback of this method is that it requires nuclear to heat the water: the cost is high and production depends on stocks.
Sources: